THE OVERVIEW OF THE ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
1. The functions of coolant temperature sensor
The engine coolant temperature sensor, also known as ECT is one of the very important sensors to help protect the engine, improve the working efficiency of the engine as well as help the engine stable operation.

The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor is used to measure the engine’s coolant temperature and send a signal to the ECU for the ECU to make the following adjustments:
– Correction of early ignition angle: When the engine temperature is low, the ECU will correct the advance of the ignition angle, and when the engine temperature is high, the ECU will control the reduction of the early ignition angle.
– Adjust fuel injection time: When the engine temperature is low, the ECU will control to increase the fuel injection time (increase the injector lift pulse width), When the engine temperature is high, the ECU will control the reduction of the fuel injection time.
– Controlling the cooling fan: When the coolant temperature reaches approx 80-87 degree celsius, ECU controls the engine cooling fan to start at low speed (slow speed level), When the coolant temperature reaches approx 95-98 degree celsius, the ECU controls the high-speed (high speed level) cooling fan.
– Idle speed control: When the engine is first started, the engine temperature is low. The ECU controls the idling valve (or electronic throttle) to expand to run at a fast idling speed (engine speed reaches approx. 900-1000 RPM) to warm up the engine to reduce friction between engine components and quickly achieve stable operating temperatures.
– Shift control: The ECU controls the automatic transmission using an additional coolant temperature sensor signal to control the gear shift, if the coolant temperature is still low, the automatic transmission’s ECU will not control the transmission shift to OD position.
– In addition, the ECT signal is also used to alert the coolant temperature meter (older cars use their own water temperature alarm).
Signals from the coolant temperature sensor are also used to control the exhaust gas recirculation system (EGR), control the state of the fuel injection system (Open Loop – Close Loop), control signal interruption A/C (air conditioner) when the coolant temperature is too high….
In some vehicles, in addition to the main coolant temperature sensor mounted on the engine body, there is also a ECT mounted on the coolant tank or the outlet of the thermostat, for the purpose of monitoring the working of thermostat valve (the electrical thermostat valve).
2. The structure of ECT
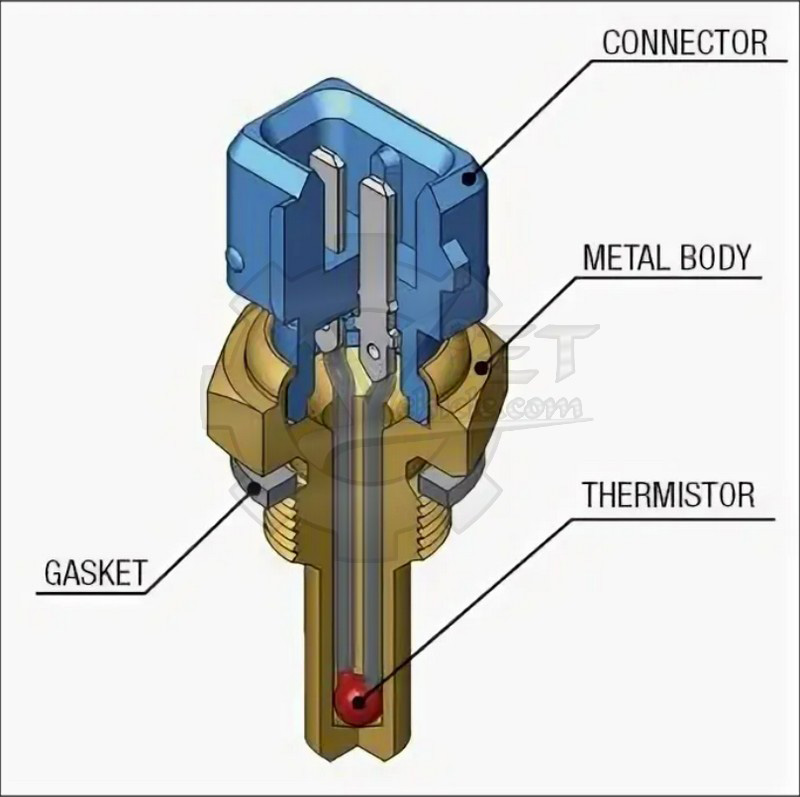
The structure of the ECT sensor is a hollow cylinder with an external thread, inside is a thermistor with a negative temperature coefficient of resistance. (resistance increases when the temperature is low and vice versa).
3. Working principle
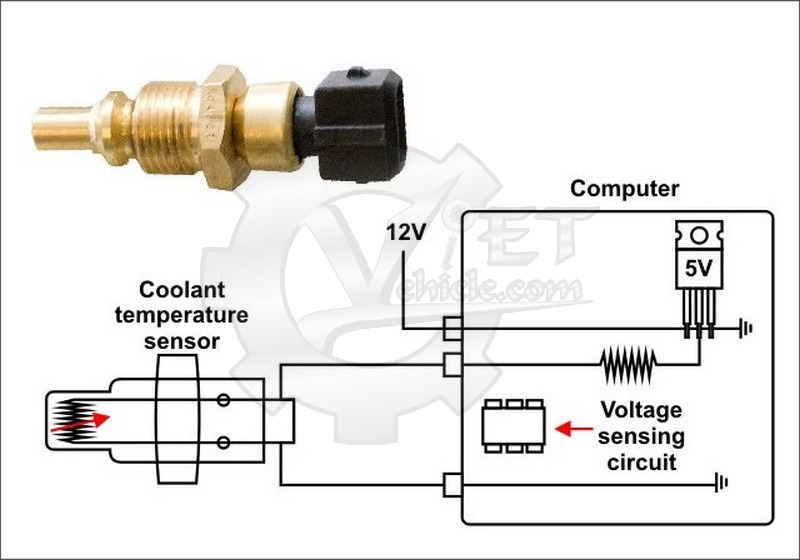
The coolant temperature sensor is located in the engine water compartment, in direct contact with the engine water. Because of the negative thermistor coefficient, when the coolant temperature is low, the sensor resistance will be high and vice versa when the coolant temperature increases, the resistance of the sensor will decrease. Changing the resistance of the sensor will change the voltage applied at the sensor pin.

The 5V voltage through the standard resistor (this resistor has a constant value according to temperature) to the sensor and then returns to the ECU to ground. Thus, the reference resistor and thermistor in the sensor form a voltage divider bridge. The midpoint voltage of the bridge is fed to an analog-to-digital converter (ADC – Analog to Digital converter).

When the engine temperature is low, the sensor resistance value is high and the voltage sent to the ADC converter is large. The voltage signal is converted into a series of square pulses and decoded by the microprocessor to notify the engine ECU that the engine is cold. When the engine is hot, the value of the sensor resistance decreases, leading to a decrease in the applied voltage, informing the engine ECU that the engine is hot.
When the engine temperature is low, the sensor resistance value is high and the voltage sent to the ADC converter is large. The voltage signal is converted into a series of square pulses and decoded by the microprocessor to notify the engine ECU that the engine is cold. When the engine is hot, the value of the sensor resistance decreases, leading to a decrease in the applied voltage, informing the engine ECU that the engine is hot.
4. Specifications
– At a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius: R = 2-3 KΩ
– At a temperature of 100 degrees Celsius: R = 200-300Ω
5. Circuit diagram of coolant temperature sensor
The coolant temperature sensor usually has 2 wires, some cars have a thermistor to report the coolant temperature on the instrument cluster combine with the coolant temperature sensor, so we see there are 3-wire or 4 wires types.

6. Check and test the ECT
Test the engine coolant temperature sensor resistance must vary with temperature according to the manufacturer’s data sheet. You can use a cup of hot, cold water or take a lighter over the sensor and check the resistance changes accordingly.
- If you use a lighter with a resistance between 0.2 and 0.3 Ω, the sensor will still work fine.
- If immersed in cold water, the resistance value increases from 4.8 to 6.6 Ω, the sensor works fine.
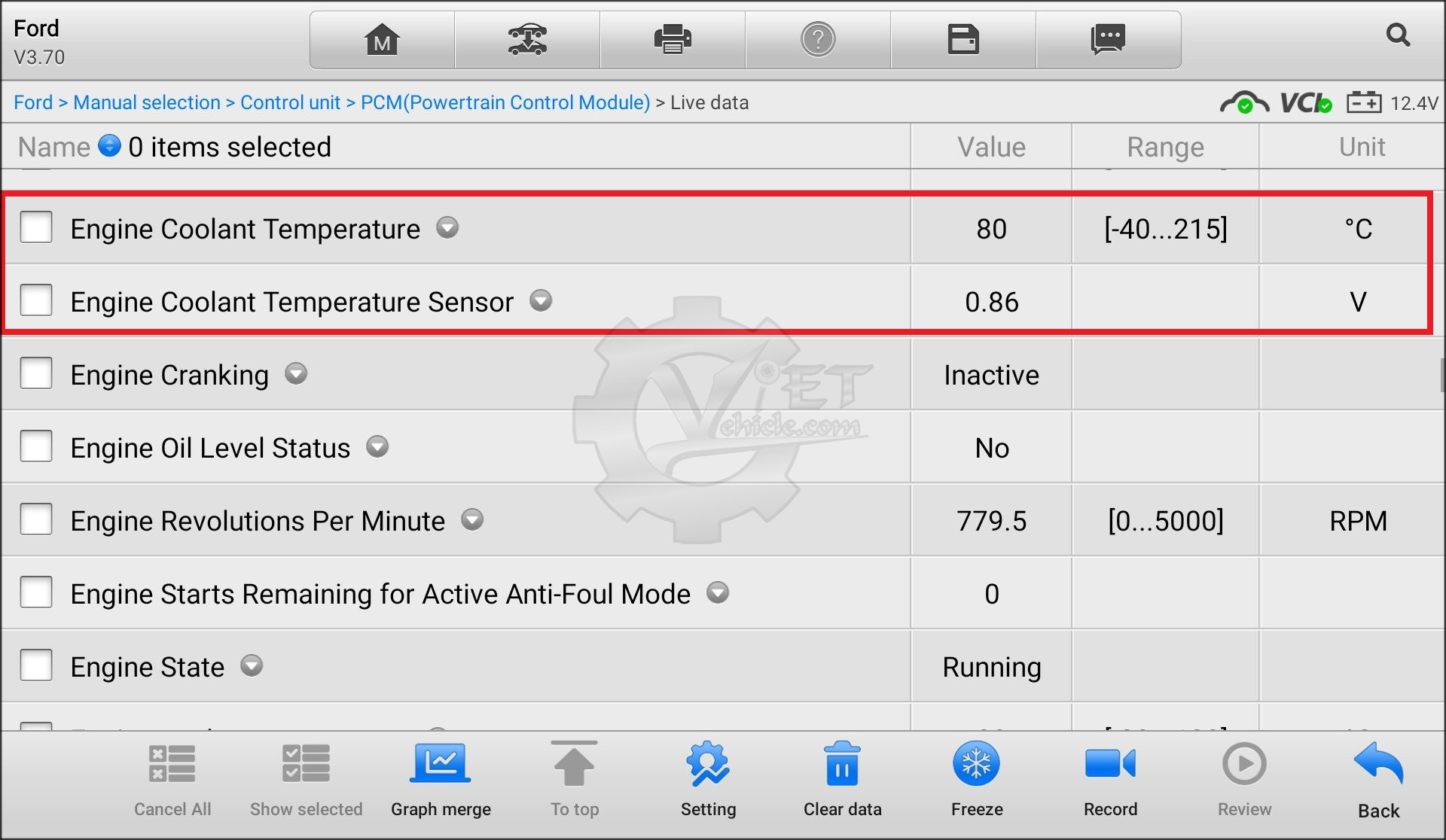
- The tester can be used to check the temperature change of the sensor when starting the engine
7. Common failures on the coolant temperature sensors
– Faulty sensor.
– Open the wire, short to the ground, short to the positive.
– Normally when the sensor circuit is open, the ECU will set at -40 degrees celcius, some sensor cars will be set at 20 degrees celcius so as not to affect the fuel injection much, avoiding too much fuel injection when the sensor circuit is faulty.
8. Practical experience when repairing
– When installing the sensor, it is necessary to check whether the water is leaking or not.
– When there is an open circuit, the coolant temperature sensor ECU understands that the coolant temperature is very low and will inject a lot of fuel, too much can overwhelm the gasoline and fail to start the engine.

9. Location of ECT
The coolant temperature sensor is located on the engine block or on the cooling water pipe, the sensor head is in contact with coolant.

Please fill in the form below, so we can provide you with an up-to-date information about our new arrivals.